Regex Parser
Features
- Implement an epsilon non-deterministic finite state automaton (ε-NFA) as the core component of the regular expression parser.
- Utilize depth first search to retrieve all states within the ε-closure and construct the transition table for the input regular expression.
- Incorporate stack-based checking to verify balanced brackets within the input regular expression.
Environment
- Java Version: JDK 11
- External Libraries: Test code would be run using JUnit 4
Outline
- Read in the regular expression
- Check the validity of the input regular expression and throw an exception if invalid
- Transform the regular expression from infix to postfix
- Build the ε-NFA
- Put the testing string into the ε-NFA built from the regex
Building Blocks
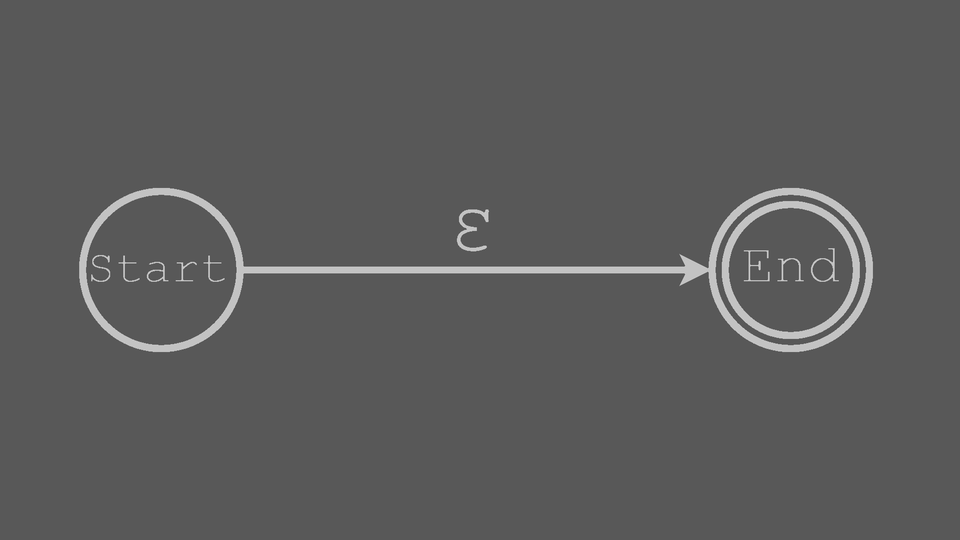
ε (epsilon)
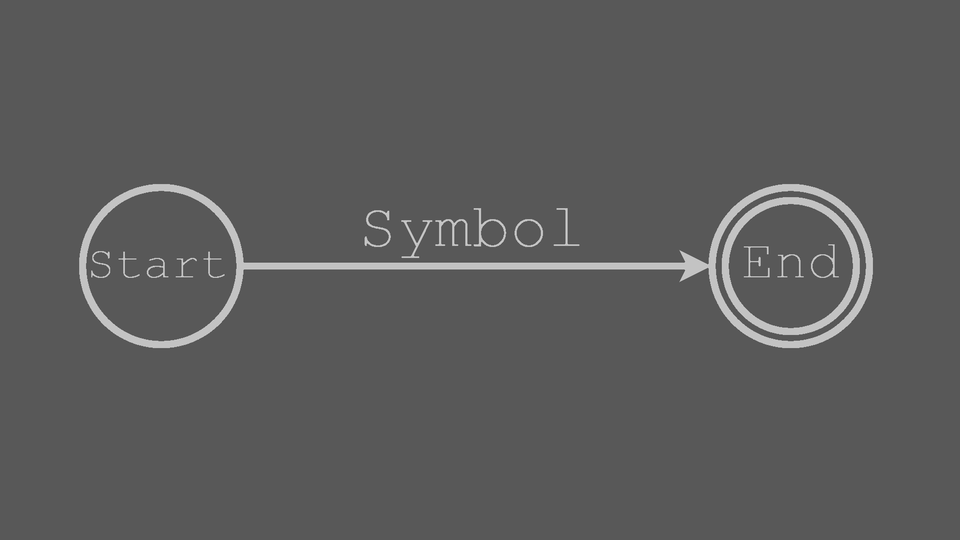
Symbol Block
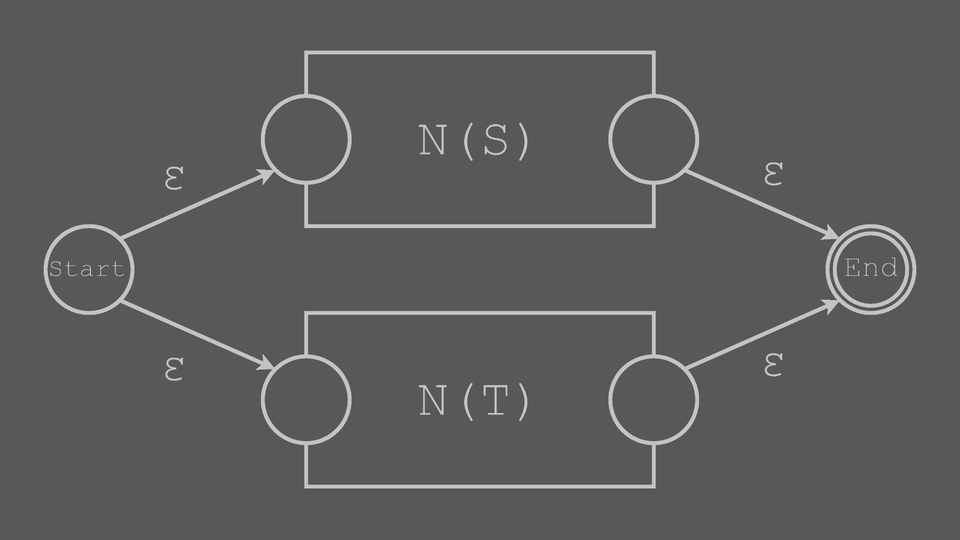
Union Block
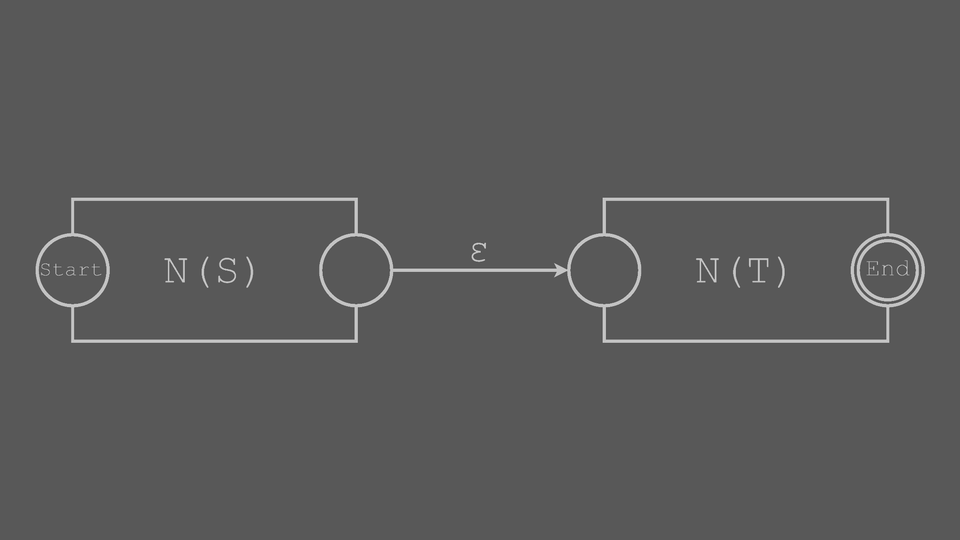
Concatenation Block
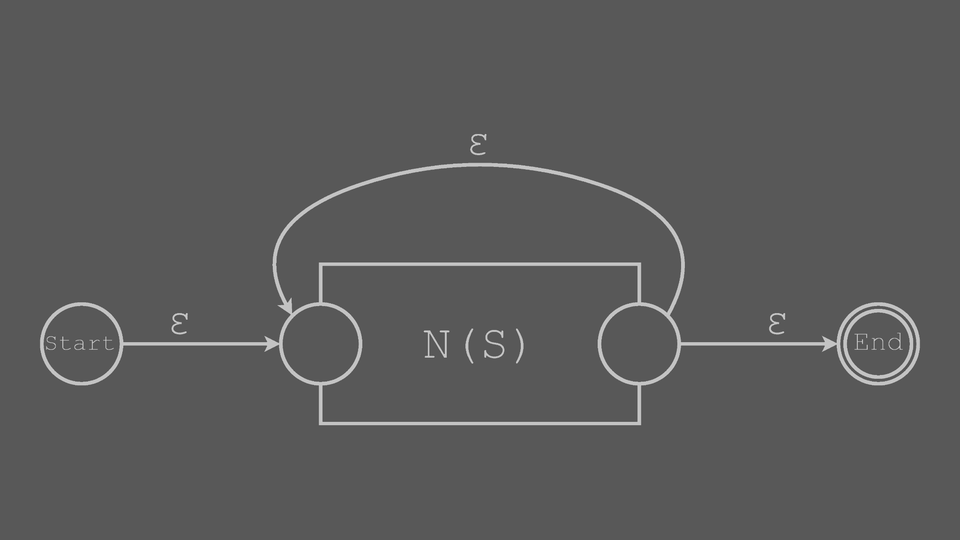
Repetition Block (Kleene Star)
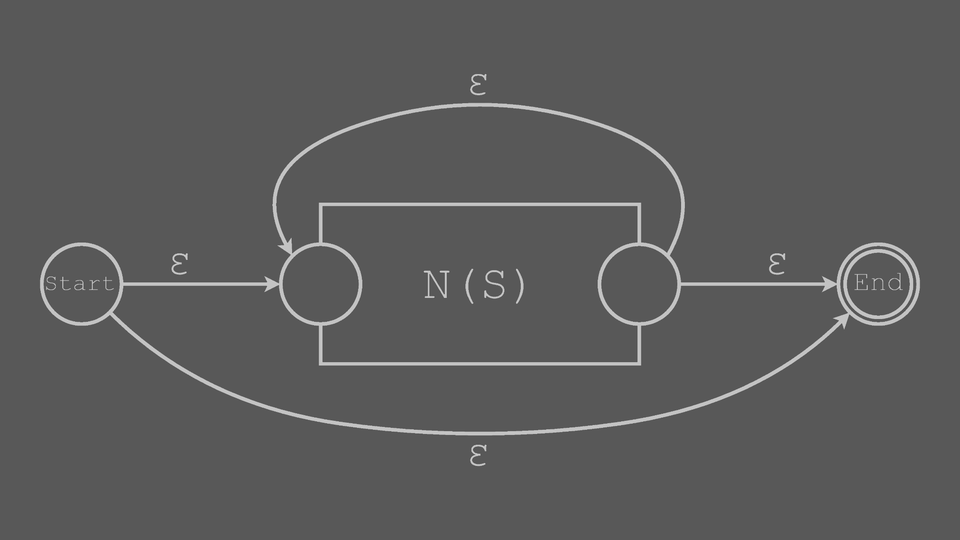
One-Or-More Block (Kleene Plus)
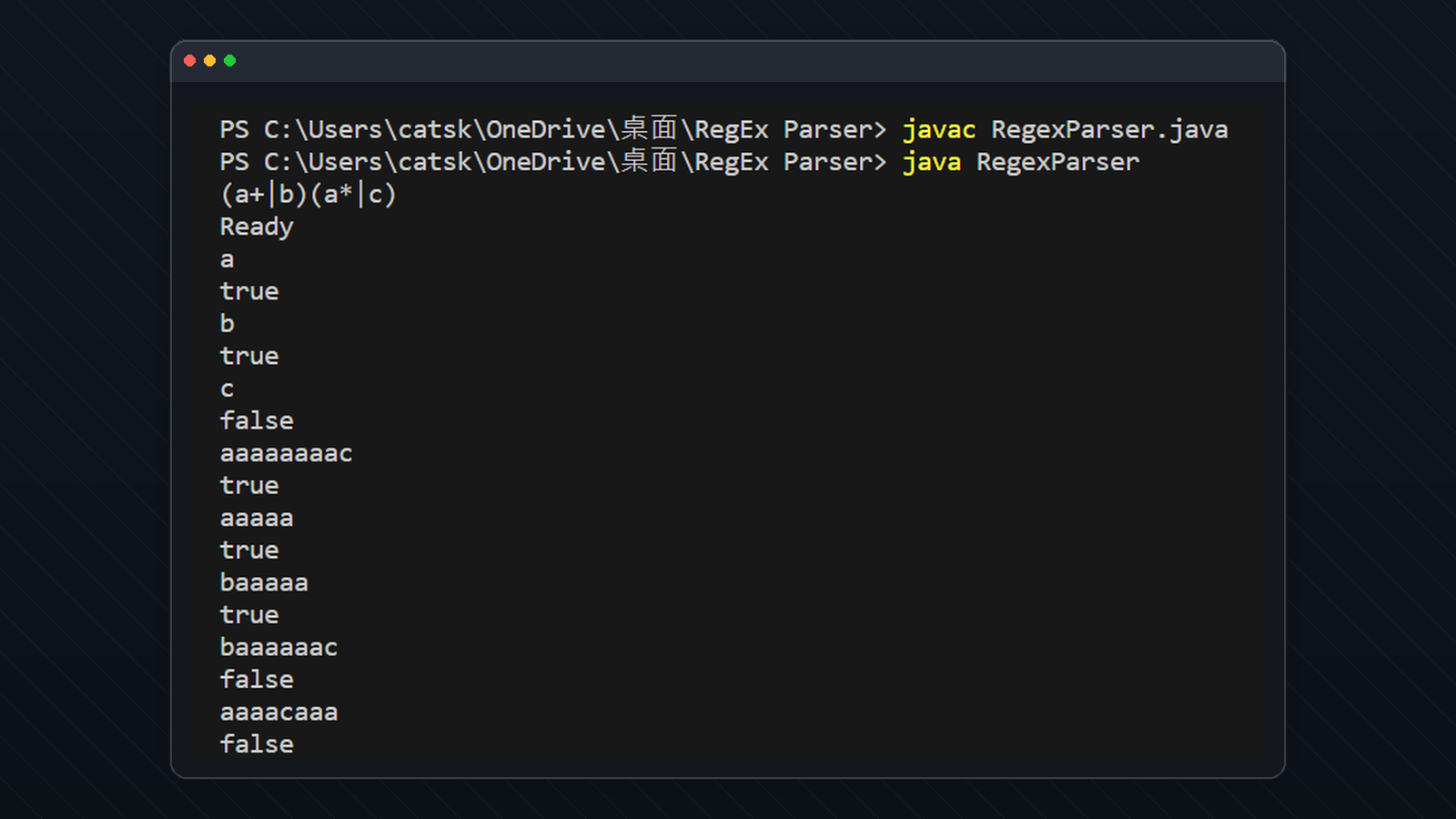
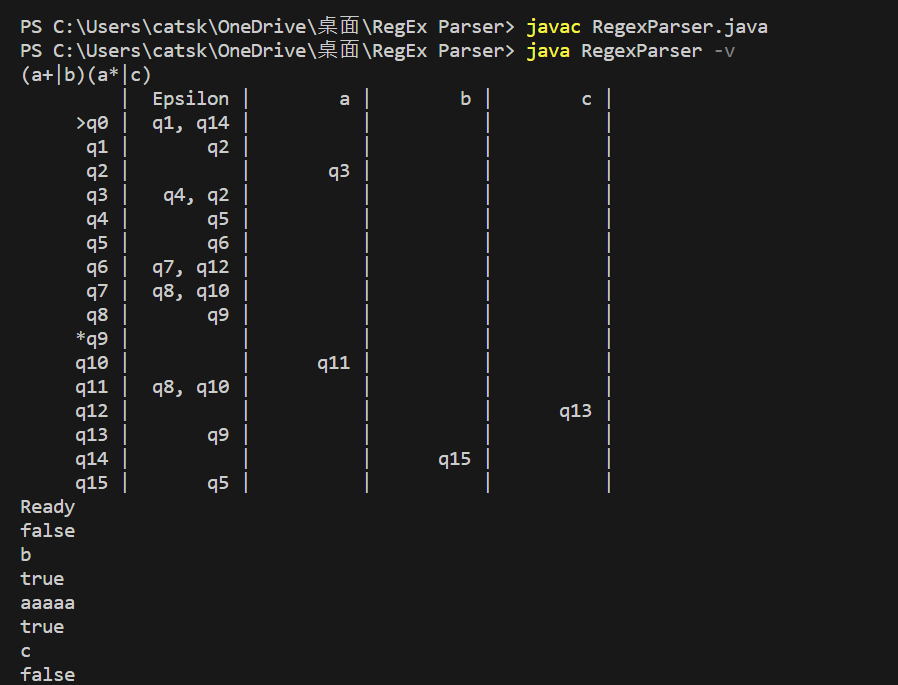
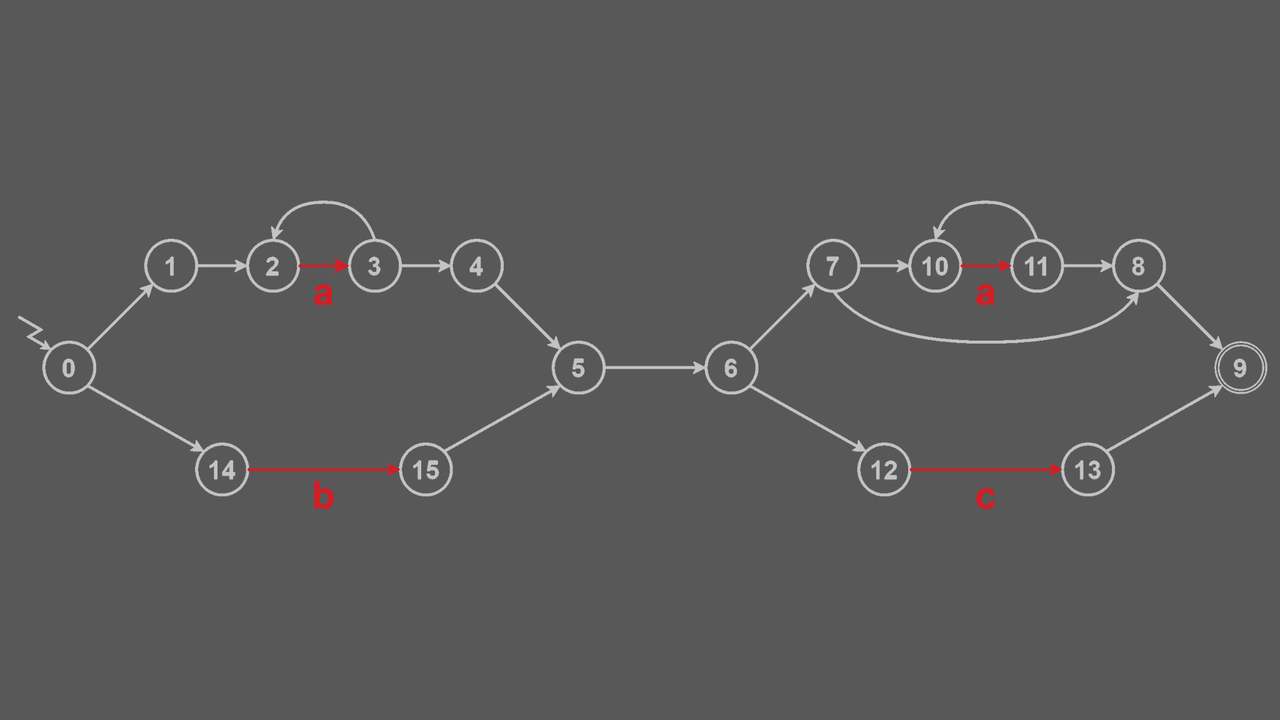
Verbose Mode Example
Regular Expression = (a+∣b)(a∗∣c)
Example Diagram
- Omit epsilon transition symbol for simplicity
- Turn symbol transition red for readability